Understanding the Soccer Pitch
Soccer is a game of precision, strategy, and passion, and the pitch is where all these elements come to life. Whether you’re a casual fan or a dedicated player, understanding the intricacies of the soccer pitch can transform how you view the game. From its historical origins to its modern-day standards, the pitch is more than just grass or turf—it’s a stage where legends are made and unforgettable moments unfold.
Soccer, often referred to as “the beautiful game,” is played on a field that is essential to its identity—the pitch. But what exactly is a pitch in soccer? Why is it called a pitch, and what makes it so unique?
In this article, we’ll explore the meaning, history, and key features of a soccer pitch, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this essential element of the sport.

What is a Pitch in Soccer?
What Does the ‘Pitch in Soccer’ Mean?
In soccer, the term “pitch” denotes the playing area where the match takes place. Unlike other sports that use terms like “field” or “court,” soccer uniquely refers to its playing area as a pitch. The word “pitch” originates from the idea of “pitching” or setting up a playing area, which dates back to the sport’s early days. The role of the pitch in soccer goes beyond just being a surface—it influences gameplay, player movement, and tactical formations, making it a crucial element in every match.
Why is a Soccer Field Called a Pitch?
The term “pitch” has historical roots that trace back to. During this time, soccer (or “football” as it’s known globally) was played on open fields, often referred to as “pitches.” The word “pitch” was used to describe the act of setting up or “pitching” the playing area, which involved marking boundaries and preparing the surface. Over time, the term stuck, and today, it’s universally recognized in the soccer world.
Historical Context
The concept of a soccer pitch evolved from informal playing fields to the standardized, rectangular surfaces we see today. Early soccer games were played on rough, uneven grounds, often shared with other sports or activities.
As the sport grew in popularity, the need for a dedicated playing area became apparent. By the 19th century, soccer pitches were formalized with clear dimensions and markings, paving the way for the modern game.
Key Features of a Soccer Pitch
Dimensions and Layout of the Soccer Pitch
The soccer pitch is a rectangular playing area with specific dimensions and layout requirements. These standards ensure consistency across games, whether played at the youth level or in professional stadiums.
Standard Dimensions
- How Long is a Soccer Pitch?
According to the International Football Association Board (IFAB), the length of a soccer pitch must be between 100-130 yards (90-120 meters). For international matches, the length is slightly narrower, ranging from 110-120 yards (100-110 meters). - How Wide is a Soccer Pitch?
The width of a soccer pitch varies between 50-100 yards (45-90 meters). For international matches, the width is standardized to 70-80 yards (64-75 meters). These dimensions ensure that the pitch is neither too cramped nor too expansive, maintaining the balance of the game.
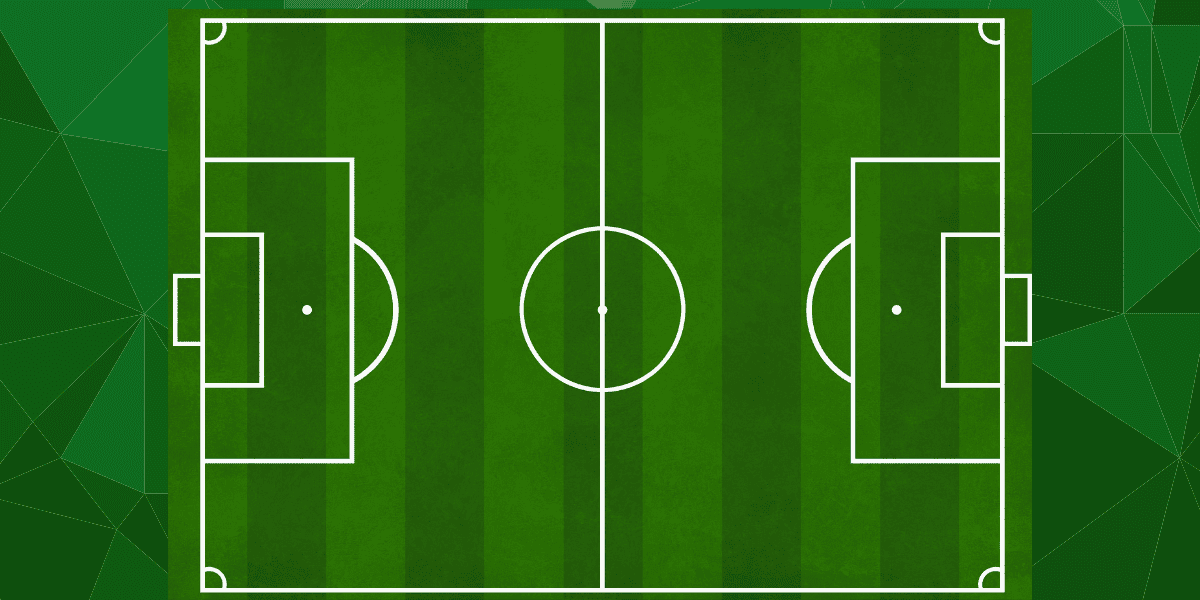
Key Elements of the Layout
The soccer pitch is divided into several key sections, each serving a specific purpose:
- Center Circle: Located at the midpoint of the pitch, this circle has a radius of 10 yards (9.15 meters) and is used for kickoffs.
- Penalty Area: Also known as the “18-yard box,” this rectangular area extends 18 yards (16.5 meters) from the goal line and is crucial for penalty kicks and goalkeeper actions.
- Goal Area: Often called the “6-yard box,” this smaller rectangle extends 6 yards (5.5 meters) from the goal line and is used for goal kicks.
- Corners: Each corner of the pitch has a quarter-circle arc with a radius of 1 yard (1 meter), marking where corner kicks are taken.
Markings and Zones on the Soccer Pitch
The pitch is marked with white lines that define its boundaries and zones. These markings are essential for gameplay and officiating.
Key Markings
- Touchlines and Goal Lines: The longer boundaries are called touchlines, while the shorter ones are goal lines. The ball must completely cross these lines to be considered out of play.
- Halfway Line: This line divides the pitch into two equal halves and is used to restart play after a goal is scored.
- Penalty Spot: Located 12 yards (11 meters) from the goal line, this spot is where penalty kicks are taken.
- Arc at the Edge of the Penalty Area: A small arc with a radius of 10 yards (9.15 meters) is drawn outside the penalty area to ensure players maintain the required distance during penalty kicks.
The Strategic Significance of the Pitch in Soccer Play
The soccer pitch is not just a playing surface—it’s a strategic battlefield. Every line, zone, and marking plays a critical role in how the game unfolds. For instance, the width and length of the pitch influence team formations and playing styles. A wider pitch allows for more wing play and stretching the opposition’s defense, while a narrower pitch favors compact, central play.
The red card in soccer is a game-changing moment that can drastically alter a team’s strategy. Within the penalty area and 18-yard box, defenders must be cautious, as reckless fouls here can lead to penalties or even a red card in soccer, leaving their team at a disadvantage.
The centre circle and halfway line are also vital, as they dictate how play restarts after a goal or at the beginning of a half. Understanding these strategic elements can enhance your appreciation of the game’s tactical depth.

Maintaining the Perfect Soccer Pitch
Maintenance for Different Surfaces (Grass, Turf, and More)
A well-maintained pitch is essential for optimal gameplay and player safety. The type of surface—whether natural grass or artificial turf—requires specific maintenance practices.
- Natural Grass: This is the traditional surface for soccer pitches, preferred for its authentic feel and player comfort. Maintaining natural grass involves regular mowing, watering, and fertilizing to ensure a smooth, even surface. In colder climates, heating systems are often installed beneath the pitch to prevent freezing.
- Artificial Turf: Increasingly popular due to its durability and low maintenance, artificial turf is made from synthetic fibers designed to mimic natural grass. While it doesn’t require watering or mowing, it needs regular brushing to maintain its texture and infill replenishment to ensure player safety.
Regardless of the surface, maintaining the pitch is a year-round commitment that involves aeration, pest control, and line marking to keep it in top condition.
Common Soccer Pitch Variations
Soccer pitches vary significantly depending on the level of play. Here are some common variations:
- Youth Fields: Smaller in size, youth pitches are designed to accommodate younger players. The dimensions typically range from 30-50 yards in width and 50-80 yards in length, ensuring the game is accessible and age-appropriate.
- Amateur and Recreational Fields: These pitches are often multi-purpose and may not adhere strictly to professional standards. They can vary in size but generally fall within the IFAB guidelines.
- Professional Stadiums: These pitches are meticulously maintained and adhere to the highest standards. They often feature state-of-the-art drainage systems, underground heating, and precision-cut grass to ensure optimal playing conditions.
These variations highlight the adaptability of soccer to different environments and player needs.

Terminology and Usage
What is the Correct Word to Use, and Which One is Wrong?
In soccer, the terms “pitch” and “field” are often used interchangeably, but there are subtle differences. While “pitch” is the preferred term in soccer, especially in British English, “field” is more commonly used in American English. Both are correct, but “pitch” is more specific to soccer.
What Does “On the Pitch” Mean?
The phrase “on the pitch” refers to anything happening during the game or within the boundaries of the playing area. For example, a player’s performance “on the pitch” is evaluated based on their actions during the match.
What Does “Off the Pitch” Mean?
Conversely, “off the pitch” refers to activities or events that occur outside the game. This includes player behaviour, contract negotiations, and community involvement. For instance, a player’s charitable work is considered “off the pitch” activity.
Bottom Line
The soccer pitch is the heartbeat of the game, influencing everything from strategy to player performance. Its dimensions, markings, and maintenance are carefully designed to ensure fair play and exciting matches. Whether you’re watching a youth game or a professional match, understanding the pitch’s role enhances your appreciation of soccer’s beauty and complexity.
From its historical roots to its modern-day variations, the pitch remains a symbol of the sport’s enduring legacy. So, the next time you watch a game, take a moment to admire the carefully crafted surface that makes it all possible. After all, the pitch isn’t just where soccer is played—it’s where the magic happens.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. What’s The Difference Between Field And Pitch?
A. In British English, the playing area for soccer is called a pitch, while in American, Canadian, and Australian English, the comparable term is often a playing field or sports field. Whether you call it a pitch or a field, this outdoor sports ground remains the heart of the game, where players and fans alike feel the magic of sports.
Q. Why Is Pitch Called Pitch?
A. The term “pitch” originates from Middle English “pichen,” meaning to drive or fix firmly, and was first used in the 17th century for cricket, where pitching the stumps into the ground was essential. By the late 1800s, it evolved into a noun describing the playing area for soccer, reflecting its deep roots in the game’s history.
Q. What Is the Reason for the Term ‘Pitch’ in Soccer?
A. The term “pitch” comes from the idea of the ball being “pitched” or thrown onto the playing area, a concept that evolved as the game of soccer took its modern shape in the 19th century.
